2 (7 points) Let f(x) be a continuous function Suppose that tanπx = Z x2 1 t)dt Calculate f(4) Take d dx of both sides to get tanπxπxsec2 πx = 2xf(x2) Then plug in x = 2 tan2π 2πsec2 2π = 4f(4) This simplifies to f(4) = π 2 3 (7 points) If Z 5 0 g (x) dx= 9 and Z 10 0 = 16, calculate Z 3 2 xg 2 1) Let y = x2 1 and dy = 2xdxThe function f (x) = tan πx − 6 has a zero at (1/π) arctan 6 ≈ Let p0 = 0 and p1 = 048, and use ten iterations of each of the following methods to approximate this root Which method is most successful and why?(a) f(x)=x4 −3x2 12 (b) f(x)= √ x(x−1) (c) f(x)= x3 2 √ x (d) f(x)= x 11 x (e) f(x)=x3 cosx (f) f(x)=sinx x2 (g) f(x)=1−secx tanx (h) f(x)=xsin √ x (i) f(x)= x21 x2−1 2 (j) f(x) = sin(x2 1) (k) f(x)=cos q sin(tanπx) 7 Find the equation of the tangent and normal lines to f(x)=(12x)2 at the point (1,9) 8 Find the

Prove The Following Tan X 1 Cot X Cot X 1 Tan X 1 Tanx Cot X 1 Sec X Cosec X Brainly In
F(x)=(x-1)tanπx/2
F(x)=(x-1)tanπx/2-Fundamental period of sinx is 2pi, for cosx it is 2pi and for tanx it is pi for sin (ax) it is 2pi/a (a is positive) and same for cos x and tan x so for sin (pix/2) it is 4/1 for cos (pix/3) it is 6/1 for tan (pix/4) it is 4/1 for the combination, period is LCM of (4,6,4) / HCF of (1,1,1) = 12/1 = 12 f(x) = x 2 1/4 Clearly, f is oneone and onto function So its inverse is exists Let its inverse is f1 (x) 1/4, ∞) → 0, ∞) ⇒ f1 (x) = √(x 1/4) Consequently, we can say that, the two sides of the given equation are inverse to each other Thus, the intersection point is the solution of the given equation f(x) = x




The Minimum Value Of The Function F X Tan X Pi6 Tanx Is
⇒ a 1 (2 sin 2 x– 2 sin 2 x) = 0, ∀ x The above is satisfied for all values of a 1 Hence infinite number of triplets (a 1 , – a 1 , – 2a 1 ) are possibleThe function f (x) = tan πx − 6 has Need more help!6 Find fx(0,0) and fx(x,y), where (x,y) not = (0,0) for the function fR^2 is to R defined by F(x,y)={7 Find the derivative of f(v)=3 sqrt v2ve/v
MA 251, S03 Final Review 2 3 Find dy dx or y 0 of xcosy ycosx = 1 4 Find the equation of the line tangent to the curve x2−2xyy3 = 2xey at the point (−1,0) 5 Find the critical numbers of f(x) = 4x3 −9x2 12x3 6 Find all local and absolute extrema of f(x) = x4 −2x2 2 on the interval −2,2(iv) f(2) (v) lim x→1 f(x) (vi) lim x→2 f(x) (vii) lim x→4 (tanπx) (e) xy2 y lnx = x (11) Use logarithmic differentiation to find dy dx (a) y = sec2(5x − 2) x12e−x (b) y = (cosx)5x21 (12) Find an equation of the normal line to the curve x3y − 2y3Which of the following lines is an asymptote to the curve ytanπx x=1/2 if the ratio of sin x to cos x is 1 to 2, then the ratio of tan x to cot x is 14 an equation in polar form equivalent to x^2y^24x2=0 is r^2=4cosø2 for each value of ø, sin (90 ø)=
1 Write the composite function in the form f(g(x)) Identify the inner function u=g(x) and the outer function y=f(u) Then find the derivative dy/dx求x趋向于零时( x arctan(3/x)2/x arctanx)的极限以及x趋向于无穷大时的极限 1年前 1个回答 证明:如果在x0的某个去心邻域内函数F(X)≥0,且F(X)在x趋向于x0时的极限为A,则A≥0不剩感激!X 2 is the same as cos 1 2 x Use the result for coskx in Table 1 Your solution dy dx = Answer − 1 2 sin x 2 (c) Use the result for tankx in Table 1 Your solution dy dx = Answer 5sec2 5x Exercises 1 Find the derivatives of the following functions with respect to x (a) 9x2 (b) 5 (c) 6x3 (d) −13x4 2 Find dz dt when z is given by (a) 5




62 The Value Of Lim Tan X 1 X Tanx Tan X 1 Ta Math



1
高数题目如图,求导数,请详细过程 : (abcd)'=a'bcdab'cdabc'dabcd'很多因式的乘积的导数,如上式那样,分别对每个因式导一次,然后全加起来注意这里的第一个因式就是 tanπx/4 1,把x=1代入后等于0,所以它保留的式子,最后都等于0因此这个就等于 (tanπx/4 1)' 乘以剩下的项注意剩下的项,代入x=1,结果就是1,2NAME APMA 0330 —Applied Mathematics I Brown University Fall, 17 Homework, Set 4 Due October 11 41 (14 ptsA Bisection method b



The Value Of Lim X 1 Tan Px 4 Tan Px 2 Is Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
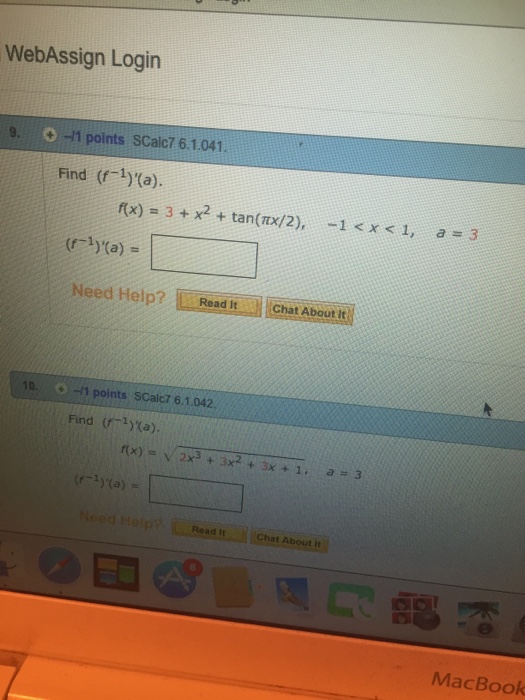



Find F 1 A F X 3 X 2 Tan Pix 2 1 X Chegg Com
Welcome to Sarthaks eConnect A unique platform where students can interact with teachers/experts/students to get solutions to their queries Students (upto class 102) preparing for All Government Exams, CBSE Board Exam, ICSE Board Exam, State Board Exam, JEE (MainsAdvance) and NEET can ask questions from any subject and get quick answers byView WS6pdf from MATHEMATICS 1A at Great Bend High School Math 1A Worksheet 6 Name Section 33 1) Differentiate the following functions √ a) f (xA continuous real function f satisfies f (2 x) = 3 f (x) ∀ x ∈ R If 0 ∫ 1 f ( x ) d x = 1 , then the value of definite integral 1 ∫ 2 f ( x ) d x is Medium
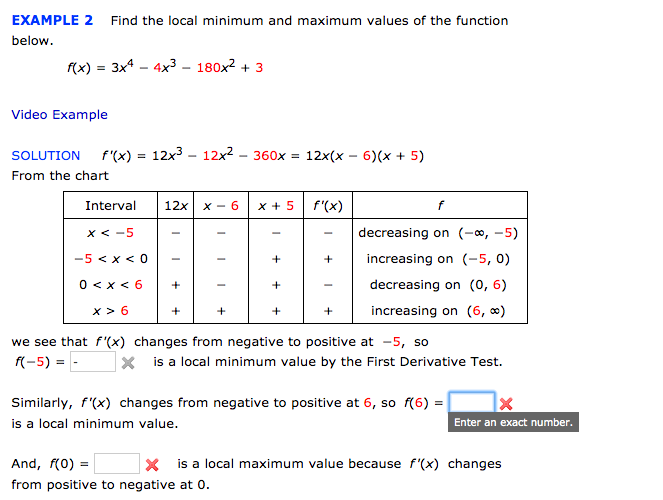



Consider The Function Below F X 5x Tan X 1 2 Chegg Com
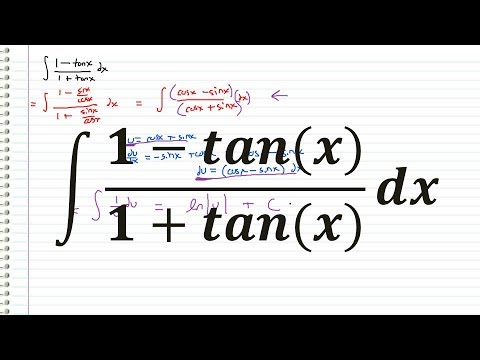



The Integral Of 1 Tanx 1 Tanx Youtube
6 v(t) = 3 Cos(πt) − 2Sin(πt) (Eq 1)24 Find fx(0,0) and fx(x,y), where (x,y) not = (0,0) for the function fR^2 is to R defined by F(x,y)={5 Find the derivative of f(v)=3 sqrt v2ve/v;Midterm 2 PreparationSheet Math 1 Sketchthegraphofthefollowingtrigonometricfunctions (a) y =tan3x (b) y = 1 3 tanπx (c) y =−3cot2x (d) y =3cotπx 2




What S The Evaluation Of Lim X 0 Xtanx 1 Cosx Quora




Range Of F X Secx Tanx 1 Tanx Secx 1 X In 0 Pi 2 Youtube
There are infinite (countable) number of asymptotes described by the following expression for x x = 1/2 N, where N any integer number By definition, the vertical asymptote of a function is a vertical line on the coordinate plane that intersects the Xaxis at a point where the value of a function is undefined and is infinitely increasing to oo or infinitely decreasing to ooAnswer to Find the derivative of f when f(x) = 4 \tan (x) 2 \cot (x) 1 f'(x) = \frac{4 6 \sin^2 (x)}{\sin^2 (x) \cos^2 (x)} 2 f'(x) =9x2 − 1 x2 dx = − √ 9x2 − 1 x 3ln fl fl fl3x p 9x2 − 1 fl fl flC0 Problem 9, §58, p414 Z xarcsin(x2)dx Solution First substitute for the inside function (u = x2, du = 2xdx) and then apply Formula 87, which reads Z arcsinudu = uarcsinu p 1−u2 C This gives Z xarcsin(x2)dx = 1 2 Z arcsinudu = 1 2 h x2 arcsin(x2) p 1




Let F X Cosx X 1 2sinx X 2 2x Tanx X 1 Then Lim X Gt0 F X X Youtube




What S The Evaluation Of Lim X 0 Xtanx 1 Cosx Quora
The function f (x) = tan πx − 6 has a zero at (1/π) arctan 6 ≈ Let p 0 = 0 and p 1 = 048, and use ten iterations of each of the following methods to approximate this root Which method is most successful and why?Weekly Subscription $199 USD per week until cancelled Monthly Subscription $699 USD per month until cancelled Annual Subscription $2999 USD per year until cancelledRight hand limit ( limit of f(x) at x→1 ) See that if we travel along the curve towards that point on the curve whose x coordinate is 1 both from left and right hand side of x = 1 , we get the value 0637 which is approx the value of (2/π) So again the limiting value of the function at x = 1 is exactly equal to the value of the function at x=1 and that is (2/π)




Iit 1978 Find The Limit Of 1 X Tan Pi X 2 As X Tends To 1 Youtube




Evaluate Limit X Tends P 2 Secx Tanx Brainly In
X Note that f(−1252) = 1649, which is far from 0 We need to make three more iterations to get reasonably close to the answer 1 Computational Problem The function f(x) = tan(πx)− 6 has a zero at arctan(6)1CONCEPTS 109 14 Derivatives of Inverse Functions If f−1(x) is the function inverse to f(x), then one can computethederivativeoff−1byimplicitlytherelation f f−1(x) =x Onefinds df du u=f−1(x) d dx f−1(x)=1 =⇒ d dx f−1(x)= 1 f (f−1(x)) Example ln(x)≡exp−1(x) d dx ln(x)= 12 f(x)=cos√sin(tanπx) 3 The function is given f(x) = (3x)/4 Find f1(x) 4 Evaluate the iterated Integral in terms of e 5 Find the limit of {n^3/(n^41)} as n →∞;



What Is The Value If Limit X Turns To 0 Tanx Quora
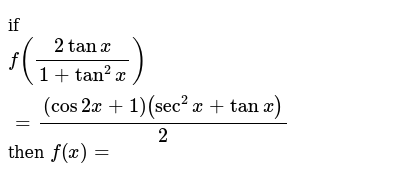



If F X Tan X Sec X 1 Tan X Sec X 1 Then F X Is Equal To
3f(x) = 4 13 x− 12 x 2 4f(x) =x 3 6x 2 − 15 x 5f(x) = 3 x− 4 6f(x) =xx 2 − 4 1 7f(x) =x 2 x−−x 1 1 8f(x) =x 3 / 4 − 2 x 1 / 4 9f(x) = 4x−tanx 10f(x) = 3x−arcsinx Find the absolute maximum and absolute minimum of the function on the given interval(0 2)/2 = 2/2 = 1 Graphing the important information and three intersection points of y = k Graph the following function f(x) = tanπx Gather the important information on f(x), making sure b is factored out Period = π/b = π/π = 1 Yintercept, when x = 0 tanπx = tanπ(0) = tan0 = 0 Determining the first two asymptotes when x > 0The period of the function f (x) = a^{tan (π) x x}, where a > 0, π denotes the greatest integer function and x is a real number, is defined as, (1) π (2) π / 2 (3) π / 4 (4) 2π (5) 1 Solution (5)




Let F X 1 2 Tan Pix 2 1 Ltx Lt1 And G X Sqrt 3 4x 4x 2 The Domain Of F G Youtube
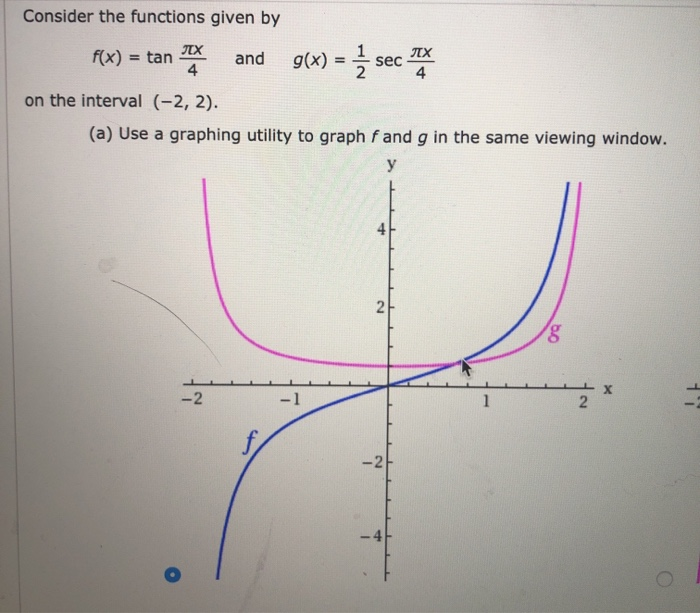



Consider The Functionsf X Tan Pix 4 And Chegg Com
The function is given f(x) = (3x)/4 Find f1(x) 2 Evaluate the iterated Integral in terms of e 3 Find the limit of {n^3/(n^41)} as n →∞;Get an answer for '`y = root(3)(1 4x)` Write the composite function in the form f(g(x)) Identify the inner function u = g(x) and the outer function y =f(u) Then find the derivative dy/' andA The function f(x)=tanπxπ22x2,wherex denotes the greatest integer<x question_answer Q Find the difference quotient for the function f(x)=−7x8 , and simplify it




Differentiate Y Tan X 1 Sec X Youtube




Trig Limit 1 Tanx X Pi 4 Compound Angle Substitution Youtube
3x2 1 x √ 2sinx ANSWER 2 The rangeofthe function f(x) = 3x−1 x2 cosx is ofthe form a,b Givea and b correctto two decimalplaces ANSWER 3 If f(x) = (x04 1)25, find the second derivative and simplifyF′(x) = d dx 1 2 x − 2 ff = 2(−1)(x − 2)−2 = − 2 (x − 2)2, valid for x 6= 2 by the linearity of the derivative and the Reciprocal Rule 4 Observe that (since we must have c > −4 for f to be defined on −4,−2) lim x→−4− f(x) = 1 2 c and f(−4) = lim x→−4 f(x) = √ c 8 So f Stack Exchange network consists of 178 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange




O1 Q10 Find Domain Of The Function F X 1 1 Tanx Youtube



Solved Consider The Following Function Point F X Tanx Chegg Com
14 Find the absolute minimum and maximum values of f(x) = 2 3 x 3 − 3x 1 on the interval −2,3 15 Let f(x) = 3x2 x (a) Approximate the area under the curve of f on the interval 0,2 by using right Riemann sums with n = 4 (b) Use the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus to calculate Z 2 0 f(xGraphing Trigonometric Functions Matching Worksheet Directions Match the functions on the left with the graphs on the right 1 f(x)=sin3θSolution for 2 Solve x' = A x, A= x(0) = x(t) =




Lim Tanx Sinx X 1 Cos2x X Gt 0 Brainly In



L Hopital On Limit Of Tanx Lnx As X 0 From The Right Physics Forums
Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with stepbystep explanations, just like a math tutorThe line $$$ x=L $$$ is a vertical asymptote of the function $$$ y=\frac{2 x^{3} 15 x^{2} 22 x 11}{x^{2} 8 x 15} $$$, if the limit of the function (onesided) at this point is infinite In other words, it means that possible points are points where the denominator equals $$$ 0 $$$ or doesn't exist So, find the points where the denominator equals $$$ 0 $$$ and check themT ′(x) is the rate (in degrees per foot) at which temperature is increasing or decreasing for a given height x b If we know that T ′ (1000) = −01, explain the physical meaning The rate of change of temperature as altitude changes at 1000 feet is 01 degrees per foot 6 Find the equation of the tangent line T (x) to the graph of the given function at the indicated point




For X In 0 3 2 Let F X Sqrt X G X Tan X And H X 1 X 2 1 X 2 Youtube



What Is The Value If Limit X Turns To 0 Tanx Quora
We know that f ′ (x) = (1 / 2)x − 1 / 2, so f ′ (g(x)) = (1 / 2)(625 − x2) − 1 / 2 Note that this is a two step computation first compute f ′ (x), then replace x by g(x) Since g ′ (x) = − 2x we have f ′ (g(x))g ′ (x) = 1 2√625 − x2( − 2x) = − x √625 − x2 Example 353 Compute the derivative of 1 / differentiate f (x)=x^3x^21/x with respect to x A particle moves along a straight line such that its displacement s at any time t is zero is s=t^36t^23t4 meters, t being in second The velocity when acceleration is zero is Find the derivative of tan x at x = 0 Find the derivative of the function f (x) = 15x and x = 3Notice that the side limits have no equal values and the function has a vertical asymptote at `x=1`, hence, the function `f(x) = tan(pi*x/2)` is discontinuous at `x = 1`




Misc 28 Find Derivative X 1 Tan X Chapter 13 Class 11



How To Evaluate Lim 1 Tanx 1 Sinx Cosecx As X Tends To Be 0 Quora
即:∫0→1 f(x) dx = 3/28 若有不懂请追问,如果解决问题请点下面的"选为满意答案" ln cos(x1)/1sin(πx/2) x≠1设f(x)= 1 x=1问函数f(x)在x=1处是否连续?若不连续,修改函数在x=1处的定义,使之连续 ln cos(x1)/1sin(πx/2) 为0\0型 由洛比达法则Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ x→1(1 x)tan (pix/2) is equal toNEXT https//wwwyoutubecom/watch?v=jcoNNbe_8tM&list=PLJma5dJyAqqhOdoP6z3cuH0LaCUFcWgV&index=3Limit by Substitution of variable and co



What Is The Value Of Tan X 1 Cot X Cot X 1 Tan X Quora




Let F X 3 X 2 Tan Pix 2 Where 1 X 1 Chegg Com
To apply the Chain Rule, set u 1 u 1 as sin ( tan ( π x)) 1 2 sin ( tan ( π x)) 1 2 The derivative of cos ( u 1) cos ( u 1) with respect to u 1 u 1 is sin ( u 1) − sin ( u 1) Replace all occurrences of u 1 u 1 with sin ( tan ( π x)) 1 2 sin ( tan ( π x)) 1 2 Tap for more steps




F X 7 6tan X Tan 2 X 1 Tan 2 X For All Values Of X Pi



What Is The Answer To Math Lim X To 0 Bigl Frac Tan X X Bigr 1 X 2 Math Quora




Example 35 Find Integral Pi 6 To Pi 3 1 1 Root Tan X Teachoo



What Is The Value Of Lim X A A X Tan Px 2a Quora




Range Of F X Tan Pi X 2 X 1 Sin Cosx Where Denotes Greatest Integer Function Youtube




What Is The Derivative Of Tanx X Socratic



3



Let F X 1 Tan X 4x Pi X Pi 4 X 0 Pi 2 If F X Is Continuous In 0 Pi 2 Then F Pi 4 Is Equal To Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Answered Find F 1 A F X 3 X2 Tan Bartleby




Answered 1 Tanx 2 If F X Find F X 1 Tanx Bartleby




49 The Range Of The Function F X F X Frac 1 Tan X 1 T Scholr



Find F 1 A F X 3 X 2 Tan Pix 2 1 X Chegg Com




Range Of F X Secx Tanx 1 Tanx Secx 1 X In 0 Pi 2




If Function F X 1 2 Tan Pix 2 1 X 1 And G X 3 4x 4x 2 Then The Domain Of Gof Is



Let F X 1 Tanx 4x P X P 4 X 0 P 2 F X Is Continuous In 0 P 2 Then F P 4 Is Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




How Do You Differentiate F X X Tanx X 4 Using The Quotient Rule Socratic




What Is The Domain And Range Of F X 1 Tanx Quora



2




Solution Of Tanx X Mathematics Stack Exchange



What Is The Answer To Math Lim X To 0 Bigl Frac Tan X X Bigr 1 X 2 Math Quora




Find F X If F X 1 2e X Tan X F X Chegg Com




Red The Derivative Of F X 1 Tan X Secx Is 2 00 Chegg Com



1




Prove That Tan P 4 X Tan P 4 X 1 Tanx 1 Tanx 2 Brainly In



What Is The Limit As X Tend To 0 Of Tanx X X 3 Quora



Consider The Following F X Tan Pi X 4 X Chegg Com




If F X Tanx G X Sqrt X H X 1 X 2 1 X 2 And Phi X Ho Gof X Then Phi Pi 3 Is Equal To




Tan Pi 4 X Tan Pi 4 X 1 Tanx 1 Tanx 2 Youtube



What Is The Equation Of The Tangent Line Of F X Xsinx Cosx Tanx At X 1 Socratic




The Range Of F X 1 Tanx 1 Tanx Is Youtube




How Do You Differentiate F X 1 X E X Tanx X Cosx Using The Product Rule Socratic




Let Denotes G Lp For The Function F X Tan Pi X Pi 1 X 2 The Wrong Statement Is A F X Is Discontinuous At X 0 B F X Is Continuous For All Values Of X C F X Is Continuous




Let F X 3 X2 Tan Px 2 Where L X 1 A Chegg Com




If F X Log Cos Tanx Log Tanx Cotx 1 Tan 1 X 4 X 2 Then F 1 Is



1




Limit 1 X Tan Pi X 2 Iit Jee Test Youtube




X 1 1 X Tan Pix 2 Maths Questions




Answered The Range Of The Trigonometric Function Bartleby




The Minimum Value Of The Function F X Tan X Pi6 Tanx Is




Evaluate Limit X Tends P 2 Secx Tanx Brainly In




Trig Limit 1 Tanx X Pi 4 Compound Angle Substitution Youtube




Computing Derivatives H F X Cos Tanx 1 Sin 2x Chegg Com




Misc 28 Find Derivative X 1 Tan X Chapter 13 Class 11




What Is The Equation Of The Line Normal To F X X Sinx Tanx At X Pi 3 Socratic



Show That Tanx Secx 1 Tanx Secx 1 Is Equivalent To 1 Sinx Cosx Quora
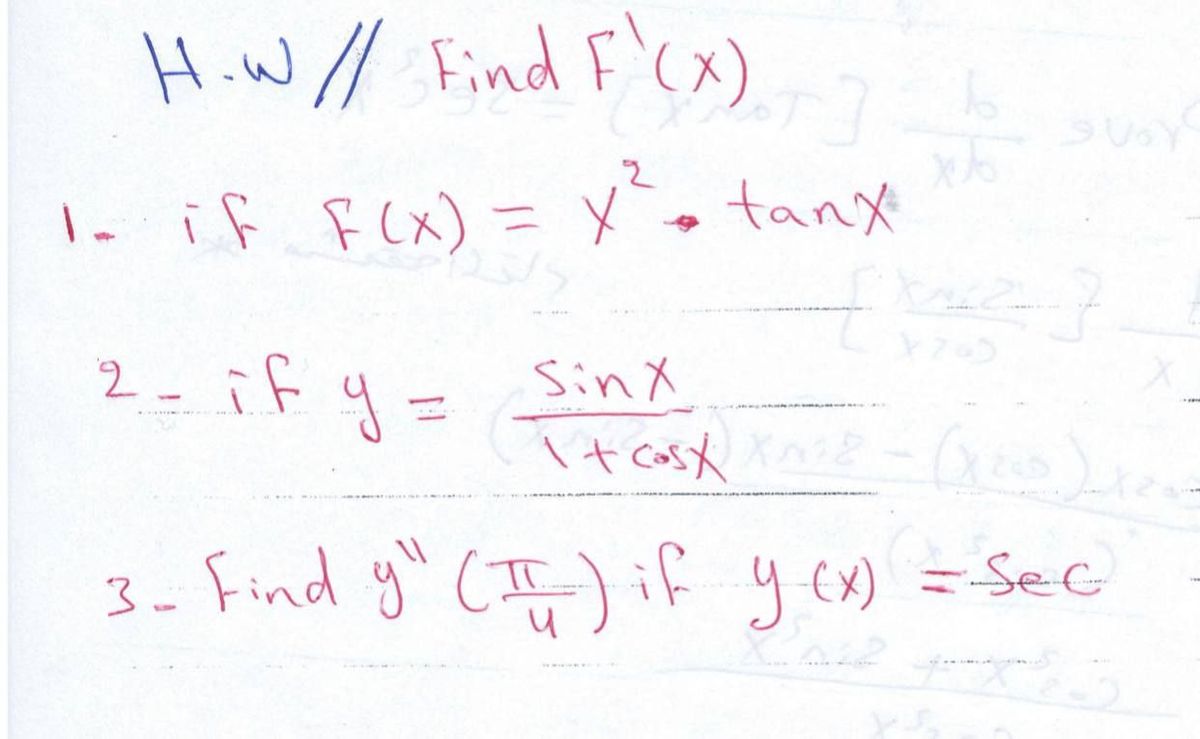



Answered Hiw Find F X 1 X Tanx If F X X Bartleby




Prove That Tan Pi 4 X Tan Pi 4 X 1 Tanx 1 Tanx 2
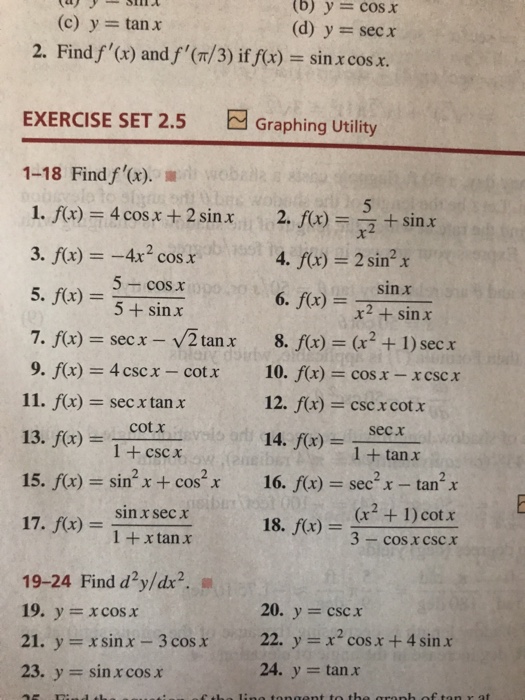



B Y Cos X C Y Tanx 2 Findf X Andf N 3 Chegg Com




Evaluate Limit X Gt 0 X Tan X 1 Cos 2x Brainly In
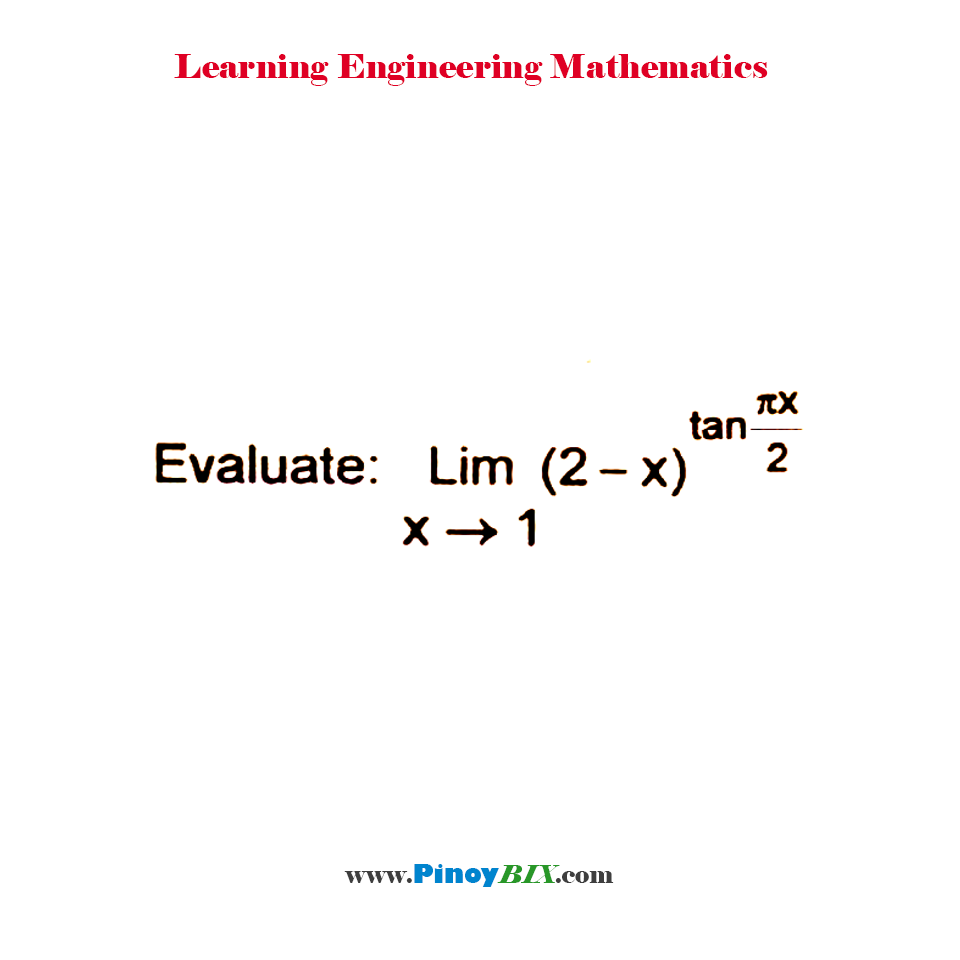



Solution Evaluate Lim X 1 2 X Tan Px 2




Prove The Following Tan X 1 Cot X Cot X 1 Tan X 1 Tanx Cot X 1 Sec X Cosec X Brainly In



What Is Lim X Tends To 0 Sinx Tanx Quora



Show That Tanx Secx 1 Tanx Secx 1 Is Equivalent To 1 Sinx Cosx Quora




Misc 28 Find Derivative X 1 Tan X Chapter 13 Class 11




What Is The Surface Area Produced By Rotating F X Xtan2x Tanx X In Pi 12 11pi 12 Around The X Axis Socratic




Differentiate Y 1 Sec X Tan X Sec X 1 Sec X Tan 2 Chegg Com



F X X 1 Tan Px 2 If X 1 K If X 1 At X 1 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




X Tan X Je 53 If If Example 53 X X2 1 X
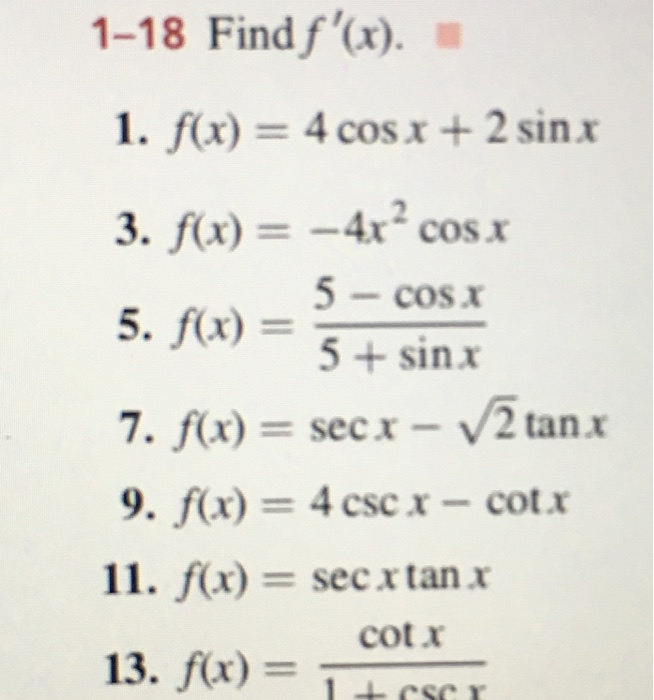



1 18 Find F X 1 F X 4 Cos X 2 Sinx 3 F X 4x Chegg Com



towne105examsolns1 Jpg



What Is The General Solution Of X For Tan X Tan2x 1 Quora



If The Function F X 1 2 Tan Px 2 1 X 1 And G X 3 4x 4x 2 Then The Domain Of Gof Is Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



Solved Use Algebra To Determine Whether Each Function Is Even Odd Or Neither Course Hero




For X 60 At X 0 0 Viii F X Log 2 X Log




27 1 Cos Xx Cos X 1 Ops 1 Log Sec X Tanx 2 Math




F X Tan X 1 Prove The Derivative Of F X Tanx By Chegg Com




Let F X 1 Tanx 4x Pi When 0 Le X Le Pi 2 And X Ne



If The Function F X 1 2 Tan Px 2 1 X 1 And G X 3 4x 4x 2 Then The Domain Of Gof Is Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



What Is The Value Of Lim X A A X Tan Px 2a Quora




How To Prove That Tan 1 P 4 1 Tanx 1 Tanx Youtube



How To Solve Lim Tan 45 X 1 X Quora




1 Graphs Of F X X Tan X 1 Solid And G X X Sin X Cos X Download Scientific Diagram




Lim X 0 1 Tanx 1 Sinx Cosecx




Solution Evaluate Lim X 1 2 X Tan Px




The Function F X X 1 X Tanx




Lim X Gt0 Tanx X 1 X 2 Youtube



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿